 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站! 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!
![]()

截止目前,引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻共30849篇,總影響因子149368.62分,發(fā)表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等頂級期刊的文獻共76篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復(fù)旦、華盛頓大學(xué)、麻省理工學(xué)院、東京大學(xué)以及紐約大學(xué)等國際研究機構(gòu)上百所。
我們每月收集引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻。若您在當(dāng)月已發(fā)表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,請致電Bioss,我們將贈予現(xiàn)金鼓勵,金額標(biāo)準(zhǔn)請參考“發(fā)文章 領(lǐng)獎金"活動頁面。
近期收錄2024年7月引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻共338篇(圖一,綠色柱),文章影響因子(IF) 總和高達1817.4,其中,10分以上文獻35篇(圖二)。
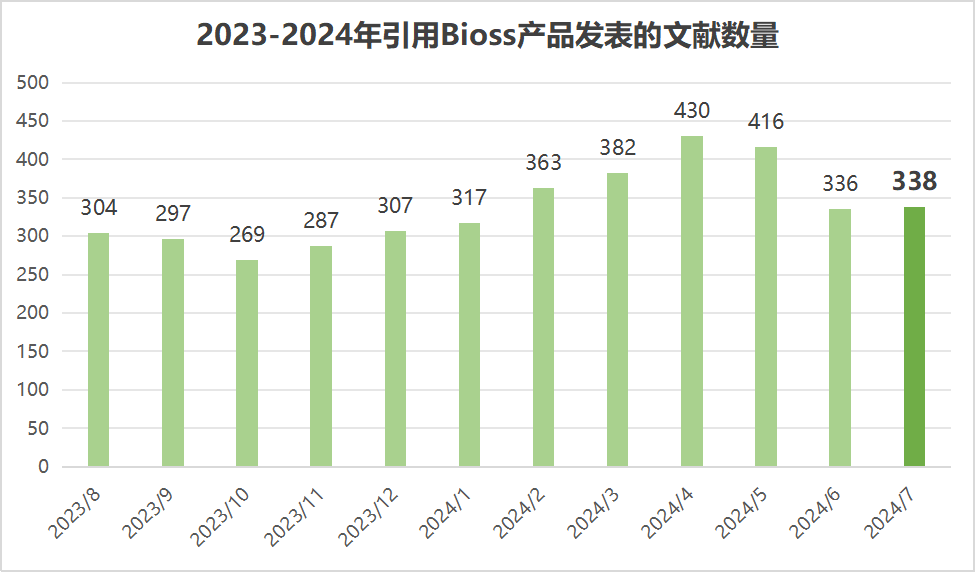
圖一
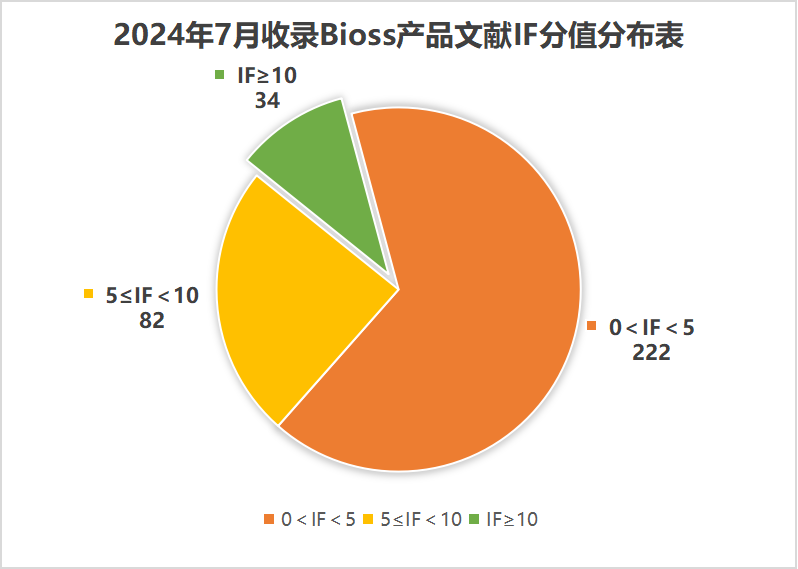
圖二
本文主要分享引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表文章至iMeta, ADVANCED FUNCTIONAL MATERIALSI, Bioactive Materials等期刊的10篇IF>15的文獻摘要,讓我們一起欣賞吧。
iMeta [IF=23.7]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
PV-0024 | Polink-2 plus®Polymer HRP Detection System (Mouse) | IHC
作者單位:中國科學(xué)院動物研究所
摘要:Emerging evidence has demonstrated the profound impact of the gut microbiome on cardiovascular diseases through the production of diverse metabolites. Using an animal model of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury, we found that the prophylactic administration of a well-known probiotic, Bifidobacterium infantis (B. infantis), exhibited cardioprotective effects in terms of preserving cardiac contractile function and preventing adverse cardiac remodeling following I/R and that these cardioprotective effects were recapitulated by its metabolite inosine. Transcriptomic analysis further revealed that inosine mitigated I/R-induced cardiac inflammation and cell death. Mechanistic investigations elucidated that inosine suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduced the numbers of dendritic cells and natural killer cells, achieved through the activation of the adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) that when inhibited abrogated the cardioprotective effects of inosine. Additionally, in vitro studies using C2C12 myoblasts revealed that inosine attenuated cell death by serving as an alternative carbon source for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) generation through the purine salvage pathway when subjected to oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation that simulated myocardial I/R injury. Likewise, inosine reversed the I/R-induced decrease in ATP levels in mouse hearts. Taken together, our findings indicate that B. infantis or its metabolite inosine exerts cardioprotective effects against I/R by suppressing cardiac inflammation and attenuating cardiac cell death, suggesting prophylactic therapeutic options for acute ischemic cardiac injury.
ADVANCED FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS [IF=18.5]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-5898R | HIF3 alpha Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:廣西醫(yī)科大學(xué)第一附屬醫(yī)院
摘要:Inflammatory infiltration of synovial M1 macrophages, high levels of ROS, and NO exacerbate osteoarthritis (OA) progression. The PdZn/CoSA-NC nanozymes, which are highly ordered PdZn intermetallic nanoparticles loaded with Co single atom N-doped carbon-rich in multi-level pores, in an attempt to serve as SOD and CAT mimicking nanozymes for OA therapy is designed. The PdZn/CoSA-NC nanozymes' high electron transfer and dual active site sufficient exposure enhances free radical adsorption and lower reaction energies, accelerating SOD-like, CAT-like, and GPx-like catalyzed reactions, outperforming CoSA-NC and PdZn/NC alone. Furthermore, PdZn/CoSA-NC nanozymes exhibit favorable biocompatibility, reduce synovial macrophage oxidative stress in OA, alleviate hypoxia, restore mitochondrial function, regulate energy metabolism, increase antioxidant factors, and reduce inflammatory factors, thus effectively mitigating the progression of OA. Mechanistically, PdZn/CoSA-NC nanozymes downregulate M1-type phenotypic markers like IL-1β by regulating purine metabolism. The PdZn/CoSA-NC nanozymes offer a novel approach to treating oxidative stress-related inflammatory diseases.
Bioactive Materials [IF=18.0]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-0549R | Collagen III Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:浙江大學(xué)醫(yī)學(xué)院附屬第一醫(yī)院
摘要:Tendinopathy leads to low-grade tissue inflammation and chronic damage, which progresses due to pathological imbalance in angiogenesis. Reducing early pathological vascularization may be a new approach in helping to regenerate tendon tissue. Conventional stem cell therapy and tissue engineering scaffolds have not been highly effective at treating tendinopathy. In this study, tissue engineered stem cells (TSCs) generated using human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUC-MSCs) were combined with microcarrier scaffolds to limit excessive vascularization in tendinopathy. By preventing VEGF receptor activation through their paracrine function, TSCs reduced in vitro angiogenesis and the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells. TSCs also decreased the inflammatory expression of tenocytes while promoting their anabolic and tenogenic characteristics. Furthermore, local injection of TSCs into rats with collagenase-induced tendinopathy substantially reduced early inflammation and vascularization. Mechanistically, transcriptome sequencing revealed that TSCs could reduce the progression of pathological angiogenesis in tendon tissue, attributed to Rap1-mediated vascular inhibition. TSCs may serve as a novel and practical approach for suppressing tendon vascularization, and provide a promising therapeutic agent for early-stage clinical tendinopathy.
Bioactive Materials [IF=18.0]
文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-0185R | PDGF-B Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:清華大學(xué)
摘要:Fungal corneal ulcer is one of the leading causes of corneal blindness in developing countries. Corneal scars such as leukoplakia are formed due to inflammation, oxidative stress and non-directed repair, which seriously affect the patients' subsequent visual and life quality. In this study, drawing inspiration from the oriented structure of collagen fibers within the corneal stroma, we first proposed the directional arrangement of CuTA-CMHT hydrogel system at micro and macro scales based on the 3D printing extrusion method combined with secondary patterning. It played an antifungal role and induced oriented repair in therapy of fungal corneal ulcer. The results showed that it effectively inhibited Candida albicans, Aspergillus Niger, Fusarium sapropelum, which mainly affects TNF, NF-kappa B, and HIF-1 signaling pathways, achieving effective antifungal functions. More importantly, the fibroblasts interacted with extracellular matrix (ECM) of corneal stroma through formation of focal adhesions, promoted the proliferation and directional migration of cells in vitro, induced the directional alignment of collagen fibers and corneal stromal orthogonally oriented repair in vivo. This process is mainly associated with MYLK, MYL9, and ITGA3 molecules. Furthermore, the downregulation the growth factors TGF-β and PDGF-β inhibits myofibroblast development and reduces scar-type ECM production, thereby reducing corneal leukoplakia. It also activates the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, promoting corneal healing. In conclusion, the oriented CuTA-CMHT hydrogel system mimics the orthogonal arrangement of collagen fibers, inhibits inflammation, eliminates reactive oxygen species, and reduces corneal leukoplakia, which is of great significance in the treatment of fungal corneal ulcer and is expected to write a new chapter in corneal tissue engineering.
Nature Cell Biology [IF=17.3]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-4296R | hnRNP K Rabbit pAb | ChIP
bs-0287R | His tag Rabbit pAb | ChIP
bs-18516R | CNBP/ZNF9 Rabbit pAb | IF
BA00208 | Cell Counting Kit-8
作者單位:中國科學(xué)院長春應(yīng)用化學(xué)研究所
摘要:Despite the demonstrated importance of DNA G-quadruplexes (G4s) in health and disease, technologies to readily manipulate specific G4 folding for functional analysis and therapeutic purposes are lacking. Here we employ G4-stabilizing protein/ligand in conjunction with CRISPR to selectively facilitate single or multiple targeted G4 folding within specific genomic loci. We demonstrate that fusion of nucleolin with a catalytically inactive Cas9 can specifically stabilize G4s in the promoter of oncogene MYC and muscle-associated gene Itga7 as well as telomere G4s, leading to cell proliferation arrest, inhibition of myoblast differentiation and cell senescence, respectively. Furthermore, CRISPR can confer intra-G4 selectivity to G4-binding compounds pyridodicarboxamide and pyridostatin. Compared with traditional G4 ligands, CRISPR-guided biotin-conjugated pyridodicarboxamide enables a more precise investigation into the biological functionality of de novo G4s. Our study provides insights that will enhance understanding of G4 functions and therapeutic interventions.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-3485R | Phospho-NFKB p65 (Ser468) Rabbit pAb | WB
作者單位:中國海洋大學(xué)
摘要:Developing strategies to target injured pancreatic acinar cells (PACs) in conjunction with primary pathophysiology-specific pharmacological therapy presents a challenge in the management of acute pancreatitis (AP). We designed and synthesized a trypsin-cleavable organosilica precursor bridged by arginine-based amide bonds, leveraging trypsin’s ability to selectively identify guanidino groups on arginine via Asp189 at the active S1 pocket and cleave the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) amide bond via catalytic triads. The precursors were incorporated into the framework of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) for encapsulating the membrane-permeable Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM with a high loading content (~43.9%). Mesenchymal stem cell membrane coating and surface modification with PAC-targeting ligands endow MSNs with inflammation recruitment and precise PAC-targeting abilities, resulting in the highest distribution at 3 h in the pancreas with 4.7-fold more accumulation than that of naked MSNs. The outcomes transpired as follows: After bioinspired MSNs’ skeleton biodegradation by prematurely and massively activated trypsin, BAPTA-AM was on-demand released in injured PACs, thereby effectively eliminating intracellular calcium overload (reduced Ca2+ level by 81.3%), restoring cellular redox status, blocking inflammatory cascades, and inhibiting cell necrosis by impeding the IκBα/NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6 and CaMK-II/p-RIP3/p-MLKL/caspase-8,9 signaling pathways. In AP mice, a single dose of the formulation significantly restored pancreatic function (lipase and amylase reduced more by 60%) and improved the survival rate from 50 to 91.6%. The formulation offers a potentially effective strategy for clinical translation in AP treatment.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-0127R | Bax Mouse pAb | WB
bs-4563R | Bcl-2 Rabbit pAb | WB
bs-0812R | IL-1 Beta Rabbit pAb | WB
作者單位:中國海洋大學(xué)
摘要:Exogenous polysulfhydryls (R-SH) supplementation and nitric oxide (NO) gas molecules delivery provide essential antioxidant buffering pool components and anti-inflammatory species in cellular defense against injury, respectively. Herein, the intermolecular disulfide bonds in bovine serum albumin (BSA) molecules were reductively cleaved under native and mild conditions to expose multiple sulfhydryl groups (BSA-SH), then sulfhydryl-nitrosylated (R-SNO), and nanoprecipitated to form injectable self-sulfhydrated, nitro-fixed albumin nanoparticles (BSA-SNO NPs), allowing albumin to act as a NO donor reservoir and multiple sulfhydryl group transporter while also preventing unfavorable oxidation and self-cross-linking of polysulfhydryl groups. In two mouse models of ischemia/reperfusion-induced and endotoxin-induced acute liver injury (ALI), a single low dosage of BSA-SNO NPs (S-nitrosothiols: 4 μmol·kg–1) effectively attenuated oxidative stress and systemic inflammation cascades in the upstream pathophysiology of disease progression, thus rescuing dying hepatocytes, regulating host defense, repairing microcirculation, and restoring liver function. By mechanistically upregulating the antioxidative signaling pathway (Nrf-2/HO-1/NOQ1) and inhibiting the inflammatory cytokine storm (NF-κB/p-IκBα/TNF-α/IL-β), BSA-SNO NPs blocked the initiation of the mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway (Cyto C/Bcl-2 family/caspase-3) and downregulated the cell pyroptosis pathway (NLRP3/ASC/IL-1β), resulting in an increased survival rate from 26.7 to 73.3%. This self-sulfhydrated, nitro-fixed functionalized BSA nanoformulation proposes a potential drug-free treatment strategy for ALI.
Journal of Magnesium and Alloys [IF=15.8]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-34032R | VEGF Rabbit pAb | WB
bsm-33235M | alpha Tubulin (Acetyl Lys40) Mouse mAb | WB
作者單位:南方醫(yī)科大學(xué)口腔醫(yī)院
摘要:The regeneration of infected bone defects is still challenging and time-consuming, due to the adverse osteogenic microenvironment caused by bacterial contamination and pronounced ischemia. Biodegradable magnesium (Mg)-based alloys are desirable for orthopedic implants due to the mechanical properties approximating those of human bone and the released Mg2+ ions essential to osteogenic activity. However, the fast and uncontrolled self-degradation of Mg alloy, along with the inadequate antimicrobial activity, limit their strength in the osteogenic microenvironment. Inspired by the structural and physiological characteristics of “fish scales," two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials, black phosphorus (BP) and graphene oxide (GO), were assembled together under the action of pulsed electric field. The bionic 2D layered BP/GO nano-coating was constructed for infection resistance, osteogenic microenvironment optimization, and biodegradation control. In the early stage of implantation, it exerted a photothermal effect to ablate bacterial biofilms and avoid contaminating the microenvironment. The blocking effect of the “nano fish scales" - 2D material superposition regulated the degradation of implants. In the later stage, it attracted the migration of vascular endothelial cells (VECs) and released phosphate slowly for in situ mineralization to create the microenvironment favoring vascularized bone formation. It is indicated that the enhancement of microtubule deacetylation and cytoskeletal reorganization played a key role in the effect of VEC migration and angiogenesis. This study provided a promising bionic strategy for creating osteogenic microenvironments that match the sequential healing process of infected bone defects.
Nature Communication [IF=14.7]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-0297G-HRP | Goat Anti-Human IgG H&L, HRP conjugated | ELISA
bs-0296G-HRP | Goat Anti-Mouse IgG H&L, HRP conjugated | ELISA
作者單位:香港大學(xué)
摘要:Human cases of avian influenza virus (AIV) infections are associated with an age-specific disease burden. As the influenza virus N2 neuraminidase (NA) gene was introduced from avian sources during the 1957 pandemic, we investigate the reactivity of N2 antibodies against A(H9N2) AIVs. Serosurvey of healthy individuals reveal the highest rates of AIV N2 antibodies in individuals aged ≥65 years. Exposure to the 1968 pandemic N2, but not recent N2, protected against A(H9N2) AIV challenge in female mice. In some older adults, infection with contemporary A(H3N2) virus could recall cross-reactive AIV NA antibodies, showing discernable human- or avian-NA type reactivity. Individuals born before 1957 have higher anti-AIV N2 titers compared to those born between 1957 and 1968. The anti-AIV N2 antibodies titers correlate with antibody titers to the 1957 N2, suggesting that exposure to the A(H2N2) virus contribute to this reactivity. These findings underscore the critical role of neuraminidase immunity in zoonotic and pandemic influenza risk assessment.
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B [IF=14.7]

文獻引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-1447R | HIF 2 alpha Rabbit pAb | IF、FC
bs-5913R | Calreticulin Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:北京大學(xué)
摘要:We prepared biocompatible and environment-friendly zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) with upconversion properties and catalase-like nanozyme activity. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) application is severely limited by the poor penetration of UV?Visible light and a hypoxic tumor environment. Here, we used ZnO NPs as a carrier for the photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) to construct zinc oxide–chlorin e6 nanoparticles (ZnO-Ce6 NPs), simultaneously addressing both problems. In terms of penetration, ZnO NPs convert 808 nm near-infrared light into 401 nm visible light to excite Ce6, achieving deep-penetrating photodynamic therapy under long-wavelength light. Interestingly, the ability to emit short-wavelength light under long-wavelength light is usually observed in upconversion nanoparticles. As nanozymes, ZnO NPs can catalyze the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in tumors, providing oxygen for photodynamic action and relieving hypoxia. The enhanced photodynamic action produces a large amount of reactive oxygen species, which overactivate autophagy and trigger immunogenic cell death (ICD), leading to antitumor immunotherapy. In addition, even in the absence of light, ZnO and ZnO-Ce6 NPs can induce ferroptosis of tumor cells and exert antitumor effects.